The 6 biggest lessons about work from 2021
If there’s one phrase we’ve heard constantly for the past two years, it’s that work will never be the same again. On the cusp of 2022, who’d have ever imagined we’d still be figuring out what that means?
In 2021, we assumed we’d return to something a little more consistent, with more concrete answers than we had in 2020. We envisioned ourselves back in offices at least a few days a week, returning to meetings (albeit with more hand sanitiser). But, for much of the workforce, things haven’t played out that way; if anything, 2021 showed us that what’s going to be ‘normal’ in the world of work is a constantly moving target.
Even as the state of work and the wider world continues to evolve, we have put our finger on a few things – chiefly, themes that pervaded work throughout 2021, and will colour the next year, and perhaps even years to come.
 Some parents feel that now they've proved remote working works, they want that flexibility to continue
Some parents feel that now they've proved remote working works, they want that flexibility to continue
The flexible-work genie is out of the bottle
It didn’t take long for huge numbers of workers to figure out how much they liked remote work, and all the elements that come with it. But in 2020, changes to work set-ups felt reactive to the pandemic, and it was hard for employees to know which shifts would stick.
A year on, it doesn’t matter what was supposed to be temporary. Workers are now living in a world with different workweek structures, asynchronous communication and permanent remote work – and now that they’ve sampled more flexibility, it’s unlikely employers can revoke the changes the pandemic has put in motion (whatever their plans once were).
Many companies are now giving staff much more freedom to choose where they work. Other firms, such as Unilever in New Zealand, and even entire countries, such as Iceland, have been experimenting with four-day workweeks. More private businesses and nations are rolling out trial programmes; Spain is expected to launch its 32-hour workweek pilot in 2022.
This change and experimentation is good for the labour force. Many report better work-life balance in more flexible arrangements (though the global average workday has got longer during the pandemic), and swaths of workers have said they’ll quit if employers call them back to the office permanently. Additionally, with more jobs open than there are job-hunters to fill them, workers currently have an outsized amount of leverage that can pressure companies to permanently keep these arrangements.
Of course, there is a possibility that some of these new work arrangements won’t stick, particularly if the labour market tightens and employees have less voice than they do now. But an overwhelming number of companies have already committed to new work practices to accommodate worker desires – a signal that stuffing the genie back into the bottle is increasingly unlikely.
 LinkedIn is among the companies that have given workers impromptu holidays during the pandemic
LinkedIn is among the companies that have given workers impromptu holidays during the pandemic
Employers are changing to meet workers’ desires – mostly
Perhaps the two loudest words of 2021: ‘Great Resignation’.
The mass worker exodus and labour reshuffle has been most extensively documented in the US, where American workers continue to leave the workforce in record numbers each month. But similar trends are staring to emerge in the UK, where workers are increasingly reporting a desire to change jobs, or are taking the plunge. (Data on the phenomenon in other countries varies; for instance, in Australia, workers are swapping jobs more than quitting en masse.)
Across the world, these workers resigning, contemplating quitting or hopping into other positions has put pressure on employers to offer better perks to both attract and retain talent. And what workers want has changed: they report asking for more personalised benefits, access to mental-health services, childcare assistance, home-work stipends and general flexibility with their work arrangements. In the US, a call for better health plans and fertility benefits has grown, too.
Many companies have stepped up to meet these desires, and more have announced plans to. Over the summer, major companies including LinkedIn and Nike shut down entirely for mental-health days and weeks – an unprecedented move in a productivity-driven, capitalist society.
Yet, there are still some holdouts who aren’t necessarily recognising or answering new calls for different perks and working arrangements. Certain sectors, such as finance and consulting, are pushing to get back to pre-pandemic business as usual. Although some of these companies have made a few less-traditional moves during the pandemic – like Jeffries Financial Group giving its staff Peloton bikes and Goldman Sachs raising base pay packets for junior bankers – leaders in some businesses are already calling workers back to their desks.
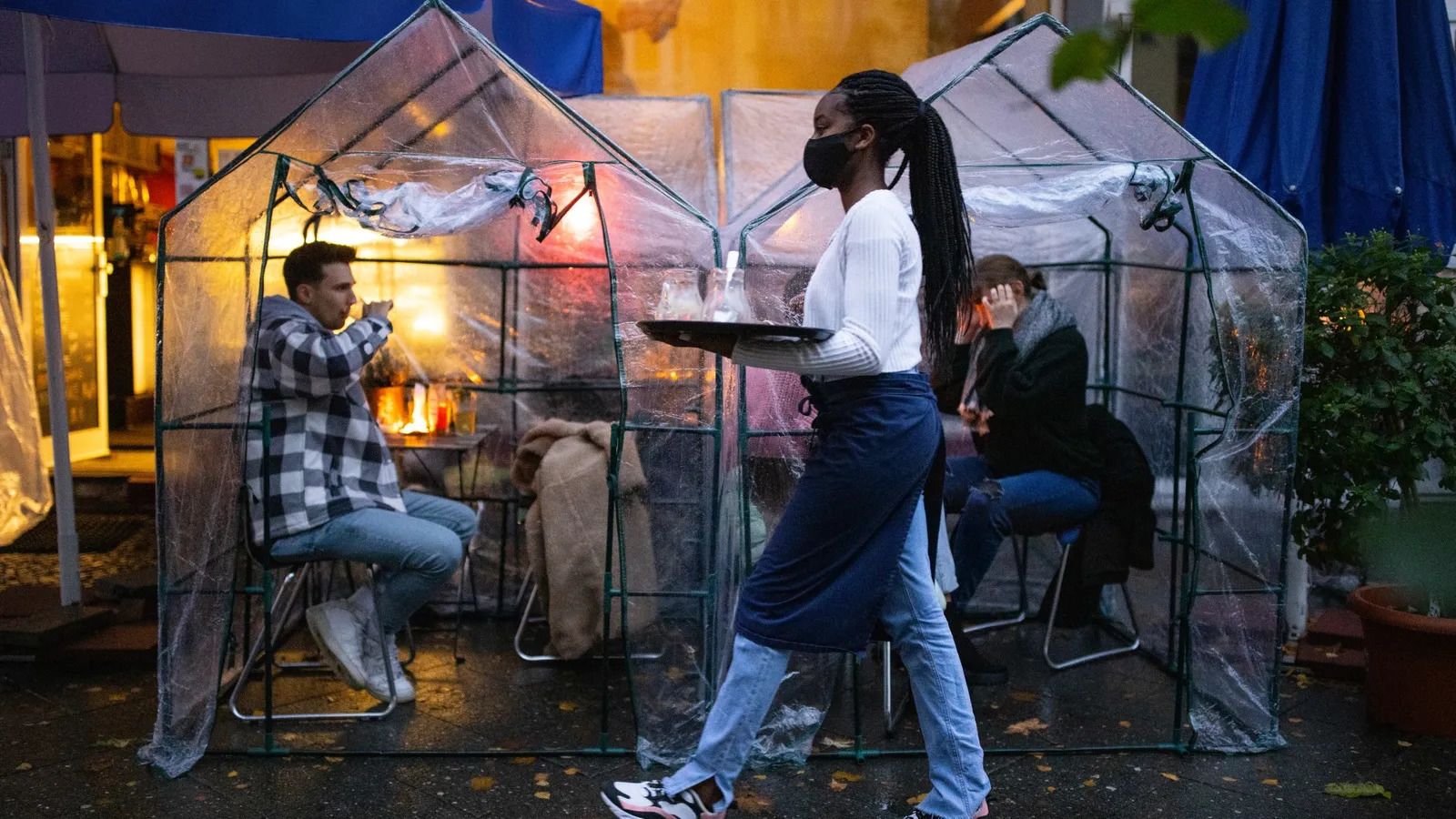 Staff shortages and new, complicated ways of working have added to the burden on some service sector workers
Staff shortages and new, complicated ways of working have added to the burden on some service sector workers
The widening inequality gap among workers
For all the benefits many workers reaped in 2021, and the growth of their sway in the labour force, not all employees have come out on top. The pandemic has exposed – and created – more inequalities.
For frontline and service workers, the return-to-work in a still chaotic and uncertain world has not been optional, and many are bearing the brunt of customers acting out. Many of these employees are stretched incredibly thin, as businesses are understaffed amid labour shortages in industries like hospitality and transport that haven’t fully recovered due to the pandemic.
We’ve also become keenly aware that access to efficient and comfortable remote work is not equal for all knowledge workers, as basic utilities like reliable high-speed internet is not a given for some employees, nor is space to work comfortably or quietly. Entry-level and younger workers in general are particularly squeezed for space – one of the reasons they’re requesting a return to office, at least a few days a week.
Inequalities for women employees have also surfaced. As in 2020, this year, women disproportionately dropped out of the workforce; in the US, as late as September 2021, hundreds of thousands of women left jobs. Even though there are some signs women’s employment is rebounding in certain sectors, growth hasn’t been on par with men, and unemployment for black women trails white women – in the US, by almost double.
There are also fears that women who are able to get back into the workforce and resume their careers may fall behind male colleagues who consistently work in the office, due to presenteeism and proximity biases – potentially worsening the gender gap.
Surfacing inequalities is the first step to change, but it’s unclear what can and will be addressed, both individually and systemically, especially when conditions are still evolving.
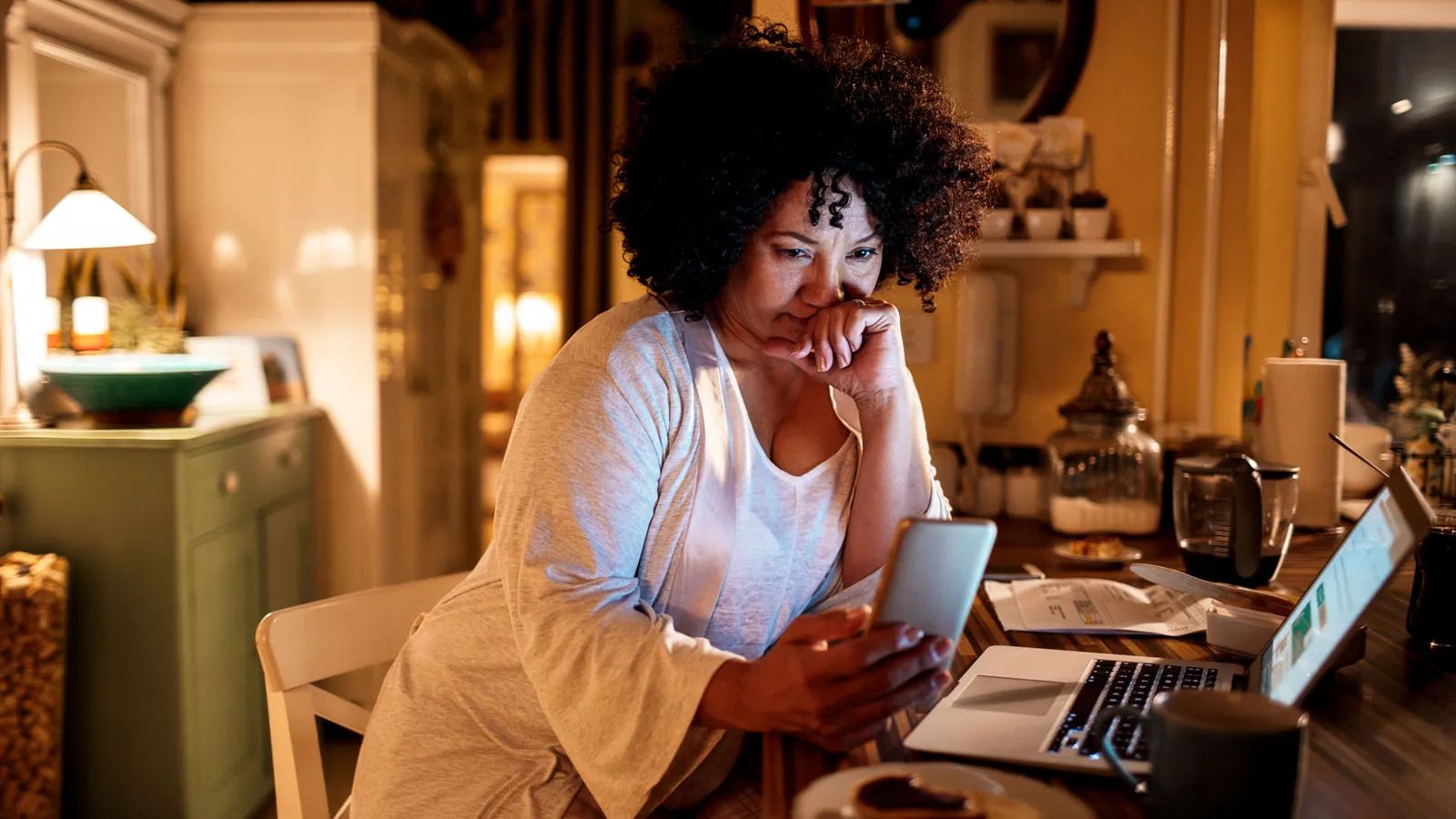 We hate saying no – and if bosses expect us on early calls or to answer late-night emails, we tend to oblige
We hate saying no – and if bosses expect us on early calls or to answer late-night emails, we tend to oblige
The heavy weight of increased poor work-life balance
Some workers have reported better work-life balance in the past year – primarily, due to remote and flexible work. But that’s not universally the case.
Without commutes to take or office doors to walk out of, many workers are finding it harder to draw hard lines between personal and professional lives. They’re reaching for their phones at all hours, answering messages in bed first-thing and sending off emails after their children go to bed. The pre-pandemic problem of presenteeism trumping productivity has found its way into the digital world. In many situations, it’s unclear whether bosses truly expect online status lights to blink green all the time, or if the pressure is coming from workers themselves – but work days have lengthened, and disconnection feels impossible, no matter the source.
Unsurprisingly, burnout and unpaid overtime are rampant, especially among certain groups such as middle-managers and women. Many businesses are running on skeleton crews amid the labour shortage, which has put an immense amount of pressure on those who stayed amid the Great Resignation.
Although some companies are trying to address issues of work-life balance, and encouraging employees to step away from their phones, it’s still culturally difficult for many to avoid overwork. So, if remote work sticks around as it seems it will, there’s no guarantee workers will press the ‘off’ button.
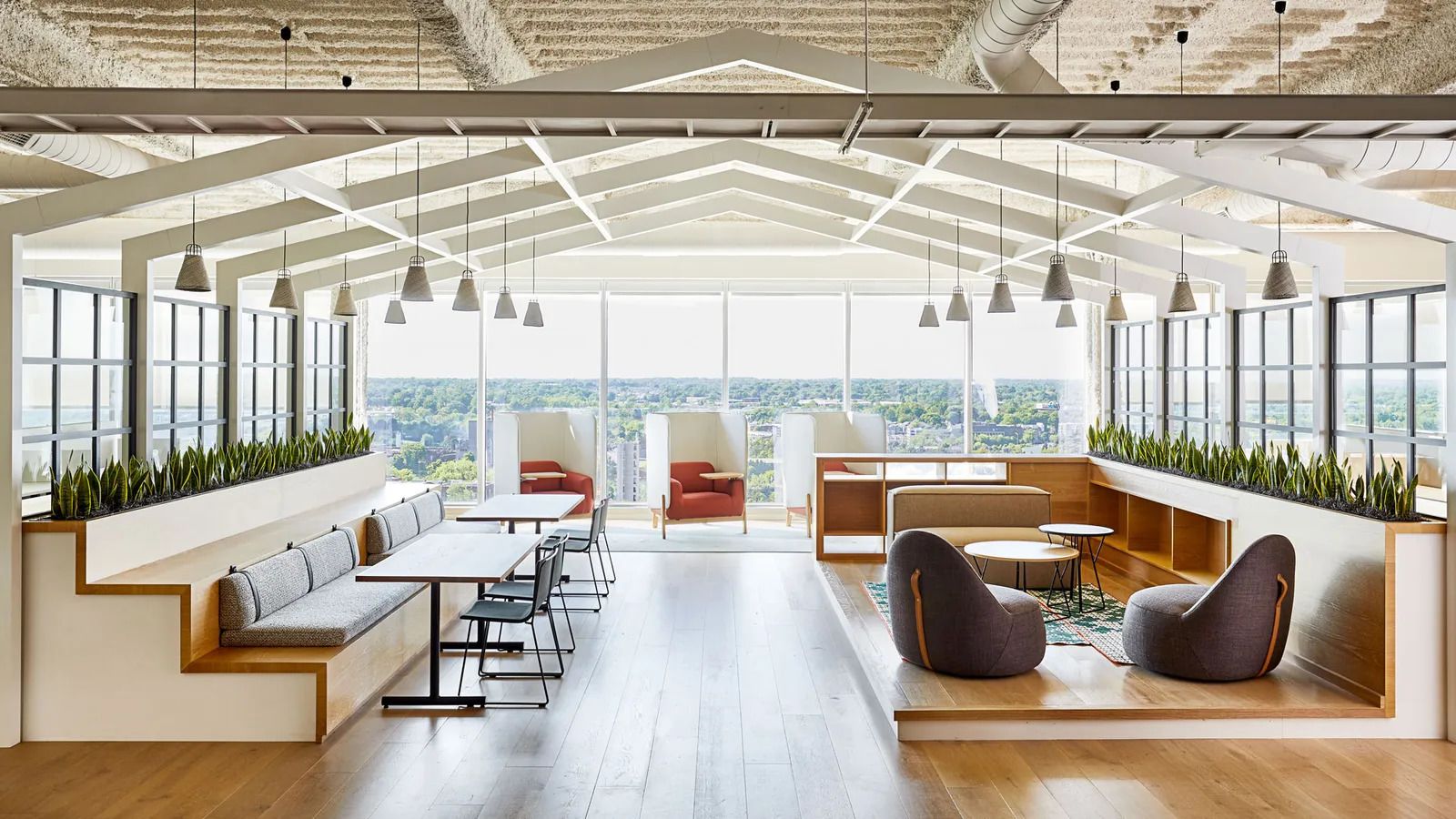 LendingTree's newly renovated office in North Carolina, US, is a
"resi-mercial" blend to create a new type of environment for returning
workers
LendingTree's newly renovated office in North Carolina, US, is a
"resi-mercial" blend to create a new type of environment for returning
workers
We’re far from perfecting hybrid
In 2021, we were supposed to kick off hybrid working in full force.
Employees and employers alike expected to gather in-person again in some form, and hit a new stride. Many companies even put money into redesigning their offices, in many cases eliminating banks of desks, and adding more collaborative spaces and isolation booths to cater to worker requests, now that the purpose of the office has changed.
Except we’re not yet in a steady hybrid pattern. The return-to-office has been patchy; certain businesses have brought workers back part time, but these policies vary widely among countries, industries and employers, and haven’t been consistent due to the continually fluctuating nature of the pandemic.
This poses challenges. First, many employees are still left in limbo without having a sense of how a hybrid set-up will – or won’t – work for them. It’s a kind of uncertainty that’s weighed down workers, both emotionally and logistically, for nearly two years. Additionally, without hybrid in action, employers lack data they need to understand what’s both successful and unsuccessful about their approaches.
As much as we continue to speculate about what will and won’t work for hybrid, we’re doing exactly that: speculating. Neither workers nor businesses have the real-life experience we need yet, which means the hybrid set-up we’re touting as the future of the workplace is very much a work-in-progress.
 For now, work is still a moving target, and we need to take our work lives day by day in lieu of concrete answers
For now, work is still a moving target, and we need to take our work lives day by day in lieu of concrete answers
Flying blind for the foreseeable future
We know by now that we likely won’t find stability in both work and broader life for a while. As new Covid-19 variants emerge, making solid plans for the future is impossible – if not almost laughable.
For instance, changing circumstances have forced the hand of companies including Google, who once had concrete plans to bring workers back in, to reverse course and announce new directives entirely. Additionally, even if life stabilises a bit more, we’re still in the throes of implementing brand-new policies, like remote- and hybrid work, that are essentially experiments whose effects and ultimate outcome is still unknown.
Looking forward to 2022, it seems the one constant will be change, whether that’s with big company policies, or day-to-day minutiae. We’re a long way from figuring out ‘normal’ – but hopefully we’ll have more answers than questions soon.