
Key facts about women’s suffrage around the world, a century after U.S. ratified 19th Amendment
This year marks the centennial of the ratification of the 19th Amendment to the United States Constitution, which guarantees women the right to vote. But the United States was hardly the first country to codify women’s suffrage, and barriers to vote persisted for some groups of U.S. women for decades. At least 20 nations preceded the U.S., according to a Pew Research Center analysis of women’s enfranchisement measures in 198 countries and self-administering territories. Today, none of these 198 countries and territories bar women from voting because of their sex; some countries do not hold national elections.
Here is a closer look at the history of women’s suffrage around the world. This analysis focuses on when women in each country won the right to vote in national elections, not regional or local elections.
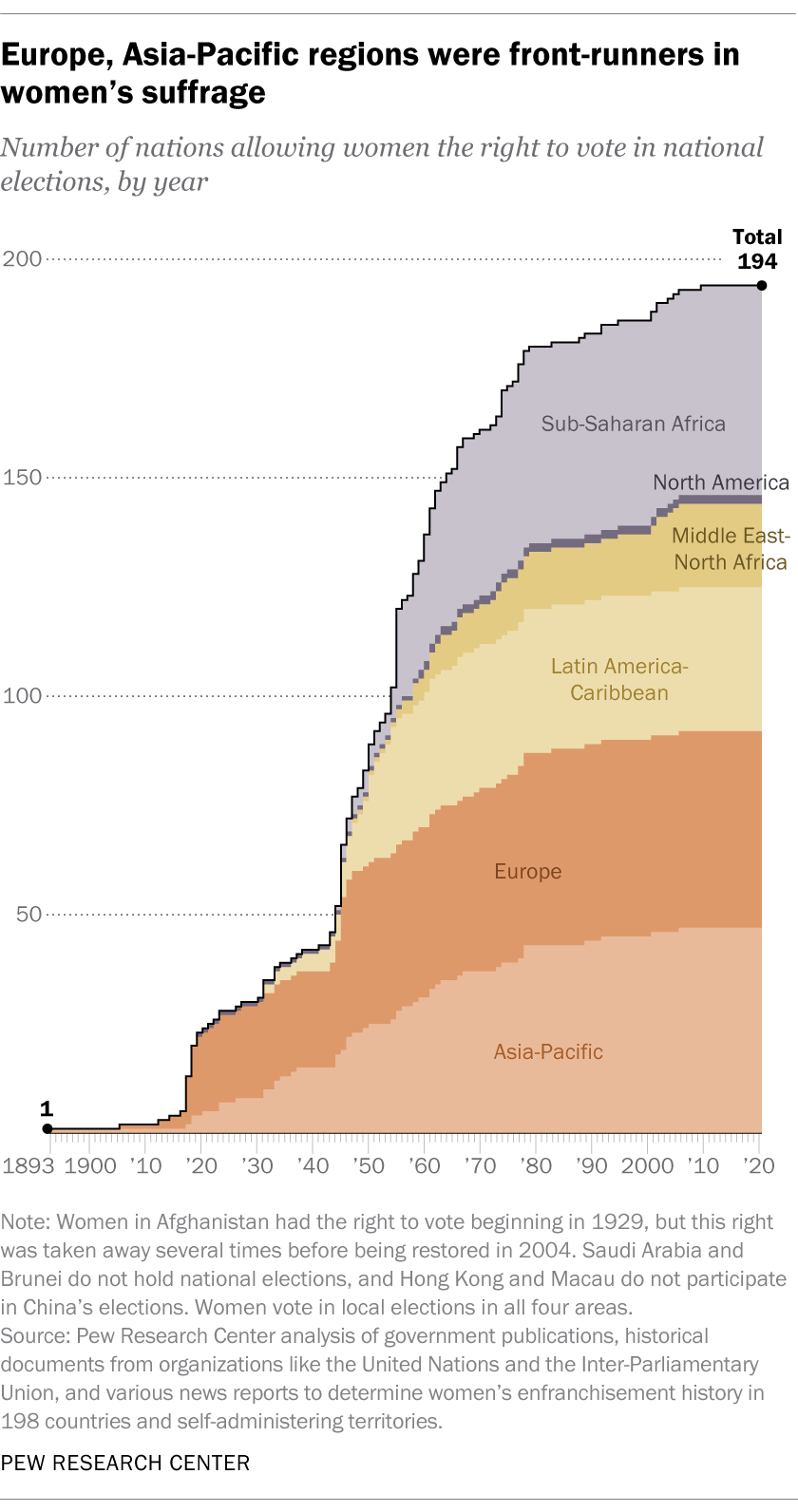
1. New Zealand enfranchised its female citizens in 1893, making it the first nation or territory to formally allow women to vote in national elections. At least 19 other countries also did so prior to the U.S. passage of the 19th Amendment in 1920, according to our analysis. These countries are spread across Europe and Asia, and about half first gave women this right while under Russian or Soviet control or shortly after independence from Russia. Russia itself extended the vote to women after demonstrations in 1917.
In at least eight additional countries, some women – but not all – gained equal voting rights in or before 1920.
2. More than half of the countries and territories we analyzed (129 out of 198) granted women the right to vote between 1893 and 1960. This includes all but six European nations. Some of the European nations that allowed universal suffrage after 1960 include Switzerland (1971), Portugal (1976) and Liechtenstein (1984).
In other world regions, women secured the right to vote in national elections only after major cultural or governmental shifts. For example, 80% of the countries in Africa we analyzed granted citizens universal suffrage between 1950 and 1975 – a period of sweeping European decolonization for the continent (as well for parts of Asia and Latin America). Many newly independent nations adopted universal suffrage along with new governments and constitutions.
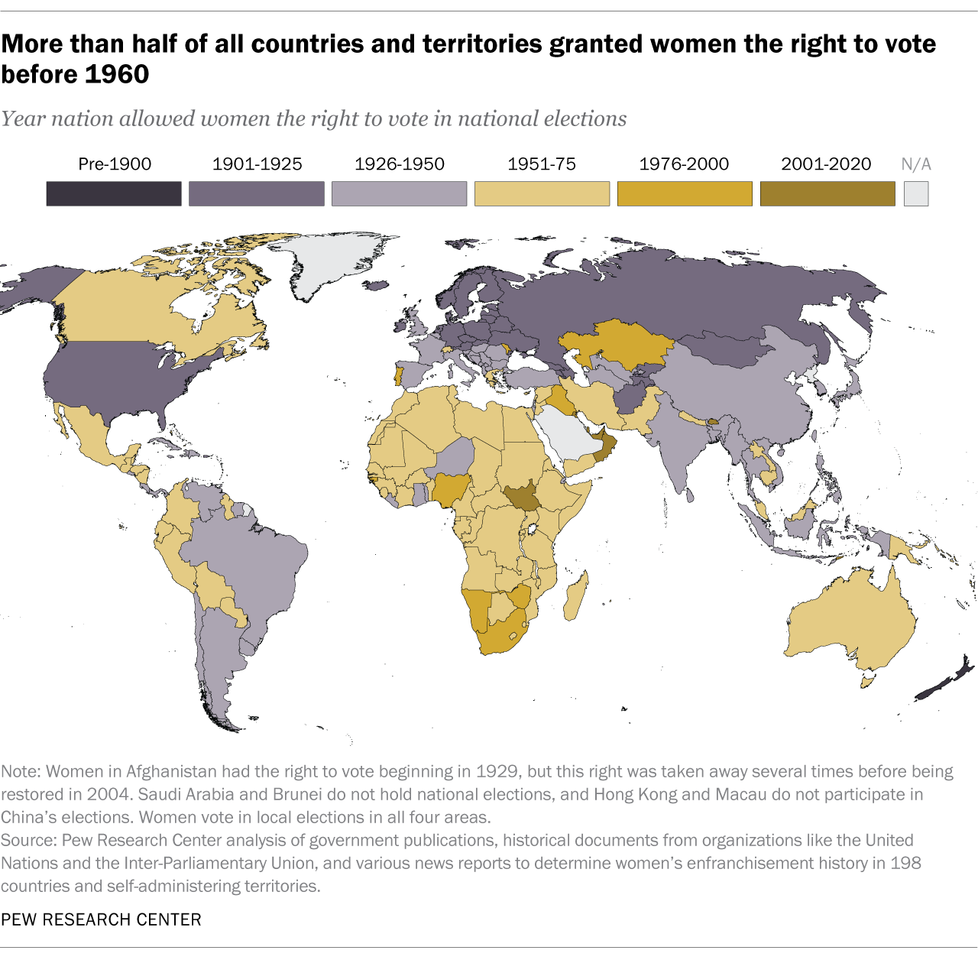
3. Bhutan, the United Arab Emirates and Kuwait are the most recent countries or territories to allow women to participate in national elections, although the picture is complicated. Bhutan and the UAE only established national elections recently. Bhutan shifted from a monarchy to a parliamentary democracy in 2007. The UAE allowed a small number of male and female citizens to vote in the country’s first national elections in 2006. In Kuwait, the country’s Parliament amended an election law in 2005; the change guaranteed women the right to vote and run for office.
In Saudi Arabia, women were enfranchised in local elections in 2015; the country does not hold national elections. South Sudan was established in 2011. It is not included among the most recent countries to give women the right to vote because women had this right starting in 1964, when the area was part of Sudan.
4. At least 19 nations – including the U.S. – initially restricted the right to vote for women of certain backgrounds based on demographic factors such as race, age, education level or marital status. Sometimes, decades passed before all citizens were enfranchised. In the U.S., for example, more than four decades passed between the ratification of the 19th Amendment and the Voting Rights Act of 1965, which took aim at discriminatory state and local restrictions intended to prevent Black Americans from voting.
Restrictions like these weren’t unique to the U.S. In Canada, for example, legislation in 1918 expanded suffrage to women, but it excluded Canadians from Asian Canadian and Indigenous backgrounds. Asian Canadians were not fully enfranchised until the 1940s, and Indigenous people could not vote until 1960.
In Australia, Indigenous women were not enfranchised until 1962, six decades after non-Indigenous women were able to vote. In South Africa, more than 60 years passed between when White women won voting rights in 1930 and when Black women won them in 1993, following the end of apartheid.
When India first expanded voting rights to women in 1935, only those who were married to a male voter, or possessed specific literacy qualifications, could vote. Universal suffrage followed in 1950.
Some countries also initially set a higher minimum age for women voters than for their male counterparts. In 1915, for example, Icelandic women over age 40 gained the right to vote. Five years later, the voting age for women was lowered to 25, in line with the requirement for men.
5. Legal and cultural restrictions limited women’s voter participation in some countries and territories even after enfranchisement. Ecuador, for instance, became the first Latin American country to grant women voting rights in 1929, but it only extended the franchise to literate Ecuadorian women, and voting was not mandatory for women as it was for men. A new constitution in 1967 made voting mandatory for literate women, and it wasn’t until 1979 that the literacy requirement was dropped completely. Several other countries, such as Hungary and Guatemala, also imposed literacy requirements on women voters that were lifted later.
More recently, Samoa’s government system allowed only those with chiefly titles, known as matai, to vote in parliamentary elections, effectively excluding women from the vote. The island nation adopted universal suffrage in 1990.
6. In some places, women were able to vote in local elections before they were enfranchised at the national level – or vice versa. In Switzerland, for example, women secured the right to vote in national elections in 1971 but had been able to vote locally in some cantons, or states, since 1959. But in another canton, Appenzell Innerrhoden, women were only given the right to vote in local elections after a 1990 federal court ruling.
7. Few countries and territories have rescinded women’s voting rights after initially granting them, but there are some notable exceptions. Afghanistan, for instance, was an early adopter of women’s suffrage after winning independence from Britain in 1919. Government shifts and instability over the next almost 100 years resulted in women losing and formally regaining the right to participate in elections several times. Women have the right to vote in Afghanistan today, but there are still barriers in place that limit their participation.
8. In many countries, including the U.S., women often turn out to vote at higher rates than men. American women have turned out to vote at slightly higher rates than men in every U.S. presidential election since 1984, according to a Pew Research Center analysis in August. The same pattern appears in other countries, too. A 2016 study of voting patterns in 58 countries by the International Institute for Democracy and Electoral Assistance found that women’s voter turnout was higher than men’s in 21 countries.











